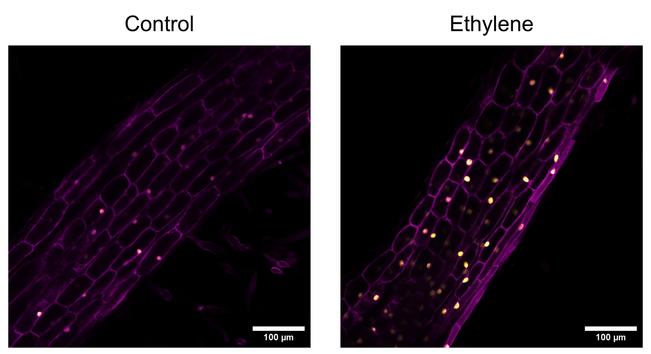
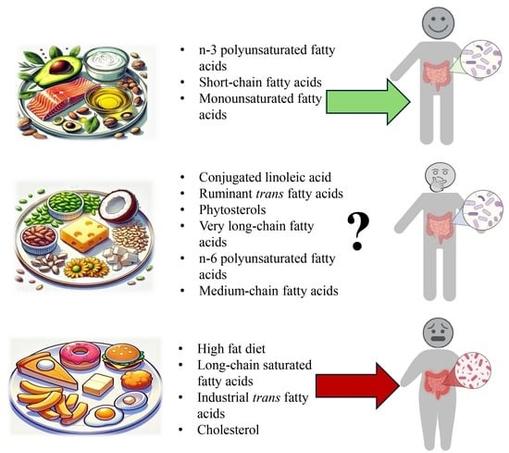
Why Do Some Poops Float Whilst Others Sink?
Okay, my peeps, let’s indulge our inner child and ask the question we’ve all asked when we were small
by @grrlscientist via #substack
#microbiome #microbiology #diet #poop #FloatingPoo #SciComm https://grrlscientist.substack.com/p/why-do-some-poops-float-whilst-others